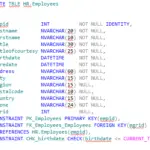
Different storage engines provide better performance in one situation over another. For general use, there are two contenders to be considered. These are MyISAM, which is the default MySQL storage engine, or InnoDB, which is an alternative engine built-in to MySQL intended for high-performance databases.
Which MySQL engine is best for performance?
Different storage engines provide better performance in one situation over another. For general use, there are two contenders to be considered. These are MyISAM, which is the default MySQL storage engine, or InnoDB, which is an alternative engine built-in to MySQL intended for high-performance databases.
Which is better InnoDB or MyISAM?
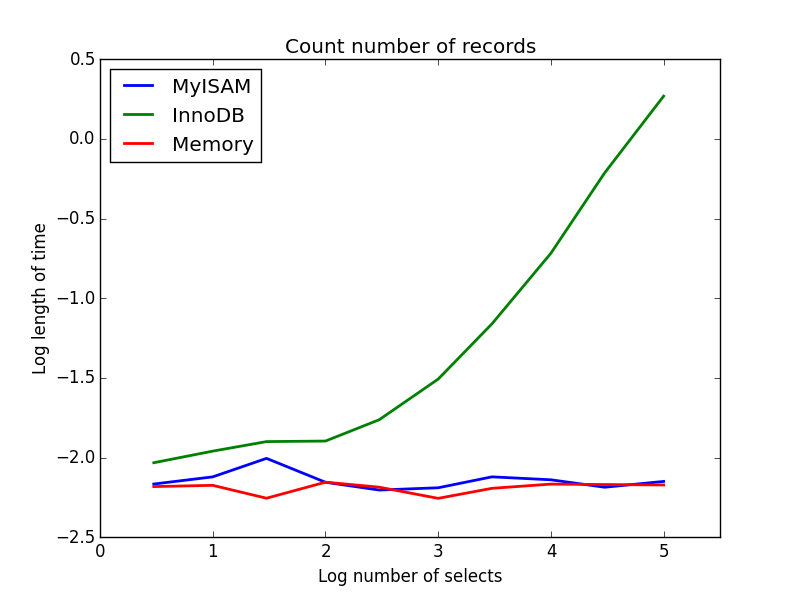
MyISAM vs InnoDBStorage: Performance InnoDB supports transactional properties, i.e. rollbacks and commits, and has a higher speed of writing. The performance of InnoDB for large volumes of data is better as compared to MyISAM. MyISAM doesn’t support transactional properties and is faster to read.
Is InnoDB faster than MySQL?
InnoDB has evolved from being a storage subsystem to a general-purpose storage engine for MySQL. Thanks to its combination of high performance and high reliability, it was made the default storage engine from Version 5.6 onwards.
Why Mylsam gives the best performance?
MyISAM is designed with the idea that your database is queried far more than its updated and as a result it performs very fast read operations. If your read to write(insert|update) ratio is less than 15% its better to use MyISAM.
Which MySQL engine is best for performance?
Different storage engines provide better performance in one situation over another. For general use, there are two contenders to be considered. These are MyISAM, which is the default MySQL storage engine, or InnoDB, which is an alternative engine built-in to MySQL intended for high-performance databases.
Which is better InnoDB or MyISAM?
MyISAM vs InnoDBStorage: Performance InnoDB supports transactional properties, i.e. rollbacks and commits, and has a higher speed of writing. The performance of InnoDB for large volumes of data is better as compared to MyISAM. MyISAM doesn’t support transactional properties and is faster to read.
Is InnoDB faster than MySQL?
InnoDB has evolved from being a storage subsystem to a general-purpose storage engine for MySQL. Thanks to its combination of high performance and high reliability, it was made the default storage engine from Version 5.6 onwards.
Is MySQL 8 faster?
As shown in the graph above, MySQL 8.0 performance shows again a huge difference in the time it takes to process transactions. The lower, the better it performs which means it’s faster to process transactions.
Which is faster 5.6 or 5.7 MySQL?
MySQL 5.7 is 3x faster than MySQL 5.6, delivering 1.6 Million SQL Queries Per Second.
Why is InnoDB slower than MyISAM?
The InnoDB Buffer Pool caches data and index pages. MyISAM only caches index pages. Just in this area alone, MyISAM does not waste time caching data. That’s because it’s not designed to cache data.
Is MariaDB better than MySQL?
When it comes to performing queries or replication, MariaDB is faster than MySQL. So if you need a high-performance relational database solution, MariaDB is a good choice. In addition, MariaDB also easily supports a high concurrent number of connections without much performance degradation.
Should I use InnoDB?
It can be used for transaction purpose i.e. all ACID properties. InnoDB can be used for row level locking, that means it gives higher performance as compared to MyISAM. InnoDB can be used for both data and index for a large buffer pool. InnoDB can be used when we need better performance than MyISAM.
What does InnoDB stand for?
A well-engineered storage engine which is now the default storage engined used by MySQL. It’s a performant storage engine providing the standard ACID-compliant transaction features. Inno stands for ‘Innovation’, InnoDB is the lesser hero underpinning the many web services and saving huge amount of DBA headaches.
What is the difference between MySQL and MariaDB?
MySQL is the largest open source database community. MariaDB is a fork from MySQL and is 100% compatible with prior versions of MySQL. However, while the charter for MariaDB remains open source and cross-platform, the future is unclear for MySQL.
What version of MySQL should I use?
We recommend using the most recent GA release. The naming scheme in MySQL 5.6 uses release names that consist of three numbers and an optional suffix; for example, mysql-5.6.
Which MySQL engine is best for performance?
Different storage engines provide better performance in one situation over another. For general use, there are two contenders to be considered. These are MyISAM, which is the default MySQL storage engine, or InnoDB, which is an alternative engine built-in to MySQL intended for high-performance databases.
Which is better InnoDB or MyISAM?
MyISAM vs InnoDBStorage: Performance InnoDB supports transactional properties, i.e. rollbacks and commits, and has a higher speed of writing. The performance of InnoDB for large volumes of data is better as compared to MyISAM. MyISAM doesn’t support transactional properties and is faster to read.
Is InnoDB faster than MySQL?
InnoDB has evolved from being a storage subsystem to a general-purpose storage engine for MySQL. Thanks to its combination of high performance and high reliability, it was made the default storage engine from Version 5.6 onwards.
Should I use MySQL 5 or 8?
MySQL 8.0 should perform better and shows to be more efficient during benchmarking. It performs very well for read/write Workload versus MySQL 5.7. There’s no reason not to use MySQL 8.0 if you’re able to upgrade. Please see the following documentation for an in-depth look into MySQL 8.0.
How much RAM should MySQL use?
The default configuration is designed to permit a MySQL server to start on a virtual machine that has approximately 512MB of RAM. You can improve MySQL performance by increasing the values of certain cache and buffer-related system variables.
Why is MySQL running slow?
Queries can become slow for various reasons ranging from improper index usage to bugs in the storage engine itself. However, in most cases, queries become slow because developers or MySQL database administrators neglect to monitor them and keep an eye on their performance.