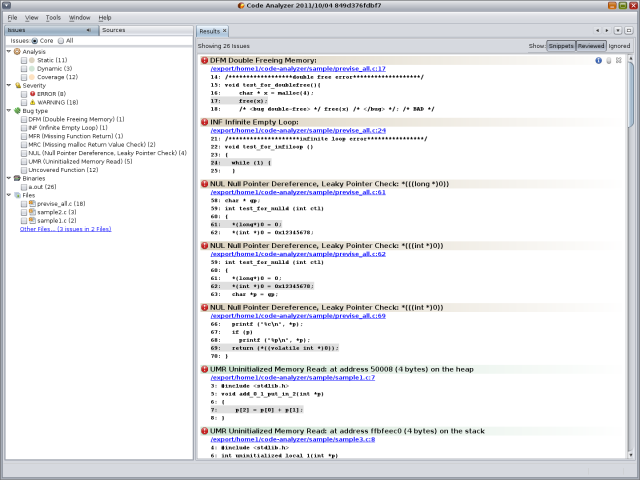
A debugger is a software tool that can help the software development process by identifying coding errors at various stages of the operating system or application development.
What checks for errors in a program?
Debugging tools are there to help identify why a program does not work correctly or as expected. When debugging, we need to work systematically and run our program with various sets of test data to find errors and correct them when we find them.
What are the 3 types of errors in a program?
When developing programs there are three types of error that can occur: syntax errors. logic errorslogic errorsLogic errors occur when there is a fault in the logic or structure of the problem. Logic errors do not usually cause a program to crash. However, logic errors can cause a program to produce unexpected results.https://www.bbc.co.uk › bitesize › guides › zcjfyrd › revisionLogic errors – Writing error-free code – KS3 Computer Science Revision. runtime errors.
What are 3 error detection techniques?
Error Detection Techniques There are three main techniques for detecting errors in frames: Parity Check, Checksum and Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC).
What are the 2 types of errors?
What are Type I and Type II errorType II errorA false negative error, or false negative, is a test result which wrongly indicates that a condition does not hold. For example, when a pregnancy test indicates a woman is not pregnant, but she is, or when a person guilty of a crime is acquitted, these are false negatives.https://en.wikipedia.org › False_positives_and_false_negativesFalse positives and false negatives – Wikipedias? In statistics, a Type I error means rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true, while a Type II error means failing to reject the null hypothesis when it’s actually false.
What is the most common method of error detection?
One of the most common techniques for detecting transmission errors is a technique known as the cyclic redundancy check (CRC).
What is error code in programming?
How many types are error?
Generally errors are classified into three types: systematic errors, random errors and blunders.
What are the 4 sources of error?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results.
What is a type error Python?
The Python TypeError is an exception that occurs when the data type of an object in an operation is inappropriate. This can happen when an operation is performed on an object of an incorrect type, or it is not supported for the object.
What are errors What are its types in computer?
There are different types of errors, or bugs , which can prevent computer programs from working in the way they should. Three of the key error types are runtime , syntax and semantic .
How do you detect and correct errors?
How to Detect and Correct Errors? To detect and correct the errors, additional bits are added to the data bits at the time of transmission. The additional bits are called parity bits. They allow detection or correction of the errors.
Which technique is used for error correction?
Error Correction can be handled in two ways: Backward error correction: Once the error is discovered, the receiver requests the sender to retransmit the entire data unit. Forward error correction: In this case, the receiver uses the error-correcting code which automatically corrects the errors.
What is error analysis method?
What is error analysis? Error analysis is a method used to document the errors that appear in learner language, determine whether those errors are systematic, and (if possible) explain what caused them.
What is the most common method of error detection?
One of the most common techniques for detecting transmission errors is a technique known as the cyclic redundancy check (CRC).
How are errors measured?
The difference between the real value and the estimated value of a quantity is known as measurement error. An error may be positive or may be negative. The deviation of the measured quantity from the actual quantity or true value is called error.
What are the two main methods of error correction?
Error Correction can be handled in two ways: Backward error correction: Once the error is discovered, the receiver requests the sender to retransmit the entire data unit. Forward error correction: In this case, the receiver uses the error-correcting code which automatically corrects the errors.
Which is the best error detection?
The best-known error-detection method is called parity, where a single extra bit is added to each byte of data and assigned a value of 1 or 0, typically according to whether there is an even or odd number of “1” bits.
What are the 2 types of errors?
What are Type I and Type II errorType II errorA false negative error, or false negative, is a test result which wrongly indicates that a condition does not hold. For example, when a pregnancy test indicates a woman is not pregnant, but she is, or when a person guilty of a crime is acquitted, these are false negatives.https://en.wikipedia.org › False_positives_and_false_negativesFalse positives and false negatives – Wikipedias? In statistics, a Type I error means rejecting the null hypothesis when it’s actually true, while a Type II error means failing to reject the null hypothesis when it’s actually false.
What are the 4 sources of error?
Common sources of error include instrumental, environmental, procedural, and human. All of these errors can be either random or systematic depending on how they affect the results.
What is an error check?
An error checking test is an aptitude test that evaluates your ability to spot errors in sets of data or text. The typical questions that arise during these assessments require an effective comparison of correct information alongside an adapted version of the original text.
What is checksum in programming?
A checksum is a value that represents the number of bits in a transmission message and is used by IT professionals to detect high-level errors within data transmissions. Prior to transmission, every piece of data or file can be assigned a checksum value after running a cryptographic hash function.