The second part of a SQL query is the name of the column you want to retrieve for each record you are getting. You can obviously retrieve multiple columns for each record, and (only if you want to retrieve all the columns) you can replace the list of them with * , which means “all columns”.
Should you use * in SQL?
That’s all about why you should not use SELECT * in the SQL query anymore. It’s always better to use the explicit column list in the SELECT query than a * wildcard. It not only improves the performance but also makes your code more explicit.
Why select * is not good?
In fact, the crime is to select all columns without thinking about it—and most ORMs readily commit this crime on behalf of their users. The reason select * actually is bad—hence the reason the myth is very resistant—is because the star is just used as an allegory for “selecting everything without thinking about it”.
What does the asterisk (*) symbol mean in SQL?
The asterisk or star symbol ( * ) means all columns. The semi-colon ( ; ) terminates the statement like a period in sentence or question mark in a question.
Should you use SELECT * in code?
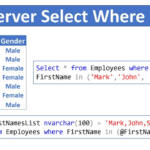
Avoid using SELECT * When writing queries, it would be better to set the columns you need in the select statement rather than SELECT *. There are many reasons for that recommendation, like: SELECT * Retrieves unnecessary data besides that it may increase the network traffic used for your queries.
What does the asterisk (*) symbol mean in SQL?
The asterisk or star symbol ( * ) means all columns. The semi-colon ( ; ) terminates the statement like a period in sentence or question mark in a question.
Which keyword is used for function * *?
Explanation: Functions are defined using the def keyword.
What is SELECT * in Oracle SQL?
A SELECT statement consists of a query with an optional ORDER BY clause, an optional result offset clause, an optional fetch first clause, an optional FOR UPDATE clause and optionally isolation level. The SELECT statement is so named because the typical first word of the query construct is SELECT.
Is SELECT * SELECT all same?
SELECT ALL means ALL rows, i.e including duplicate rows. (The opposite is SELECT DISTINCT , where duplicate rows are removed.) ALL is the default, and most people write just SELECT instead of SELECT ALL . SELECT * means all columns.
What is the difference between SELECT * and SELECT column name?
SELECT * will return 100 columns * 10 bytes worth of data while SELECT ColA, ColB, ColC will return 3 columns * 10 bytes worth of data. This is a huge size difference in the amount of data that is being passed back across the wire.
Is SELECT * faster than SELECT column?
Selecting distinct and less than all columns will always be faster than selecting *.
What is meant by SELECT *?
verb. If you select something, you choose it from a number of things of the same kind.
Is SELECT * slower than SELECT column?
For your question just use SELECT *. If you need all the columns there’s no performance difference.
What is the purpose of * In wildcard selector?
The * wildcard is known as the containing wildcard since it selects elements containing the set value. With the ^ wildcard, you get to select elements whose attribute value starts with the set value. The $ wildcard lets you select elements whose attribute values end with the specified value.
What is the symbol * used for?
We use the asterisk to point to an annotation or footnote. It can also be used as a substitute for letters in a swear word (“Oh f***!”) or to make a name anonymous (Mr M***).
Why is an asterisk (*) used here?
It is most commonly used to signal a footnote, but it is sometimes also used to clarify a statement or to censor inappropriate language.
Why is this symbol * called an asterisk?
The asterisk (/ˈæst(ə)rɪsk/ *), from Late Latin asteriscus, from Ancient Greek ἀστερίσκος, asteriskos, “little star”, is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
What is the use of count (*)?
Does count (*) ignore NULL values?
The notation COUNT(*) includes NULL values in the total. The notation COUNT( column_name ) only considers rows where the column contains a non- NULL value.
Which is an SQL * Plus command?
SQL*Plus is a command-line tool that provides access to the Oracle RDBMS. SQL*Plus enables you to: Enter SQL*Plus commands to configure the SQL*Plus environment. Startup and shutdown an Oracle database.
What does DEL * * do?
This command will delete every file (*. *) from every folder (/s) inside the Adobe folder in the user’s Documents directory. The folders will remain, but every file will get removed.
Why do we use * in text?
An asterisk is the sign *. It is used especially to indicate that there is further information about something in another part of the text. A single sentence, marked with an asterisk.