The increasing number of threads inside the cores of a multicore processor, and competitive access to the shared cache memory, become the main reasons for an increased number of competitive cache misses and performance decline.
What causes high miss rate cache memory?
The more cache levels a system needs to check, the more time it takes to complete a request. This results in an increased cache miss rate, especially if the system needs to look into the main database to fetch the requested data.
What would cause a cache miss?
A cache miss occurs either because the data was never placed in the cache, or because the data was removed (“evicted”) from the cache by either the caching system itself or an external application that specifically made that eviction request.
How is Miss rate calculated?
The miss rate is similar in form: the total cache misses divided by the total number of memory requests expressed as a percentage over a time interval. Note that the miss rate also equals 100 minus the hit rate.
What causes high miss rate cache memory?
The more cache levels a system needs to check, the more time it takes to complete a request. This results in an increased cache miss rate, especially if the system needs to look into the main database to fetch the requested data.
What is a way to reduce the miss penalty?
The smaller first-level cache to fit on the chip with the CPU and fast enough to service requests in one or two CPU clock cycles. Hits for many memory accesses that would go to main memory, lessening the effective miss penalty.
Does increasing cache size increase hit rate?
If you access many files and you have a large cache, you will have a larger cache-hit rate because older information still remains in the cache during consistency checks. However, if you have a small cache, there is less room for information to remain.
Does non blocking cache reduce miss rates?
Abstract Non-blocking caches are an effective technique for tolerating cache-miss latency. They can reduce miss-induced processor stalls by buffering the misses and continuing to serve other independent access requests.
How do I increase my cache hit ratio?
To increase your cache hit ratio, you can configure your origin to add a Cache-Control max-age directive to your objects, and specify the longest practical value for max-age .
What is a good cache hit ratio?
A cache hit ratio of 90% and higher means that most of the requests are satisfied by the cache. A value below 80% on static files indicates inefficient caching due to poor configuration.
Does the miss rate increase or decrease as the cache size increases Why?
For larger caches, increasing the block size beyond 64 bytes does not change the miss rate. However, large block sizes might still increase execution time because of the larger miss penalty, the time required to fetch the missing cache block from main memory.
Does Increased associativity always reduce the miss rate?
Associativity only affects how cache blocks are arranged, not how they are fetched from main memory, so will not affect compulsory misses.
What is miss rate in cache memory?
Similarly, the miss rate is the number of total cache misses divided by the total number of memory requests made to the cache. One might also calculate the number of hits or misses on reads or writes only. Clearly, a higher hit rate will generally result in higher performance.
How does cache size affect miss rate?
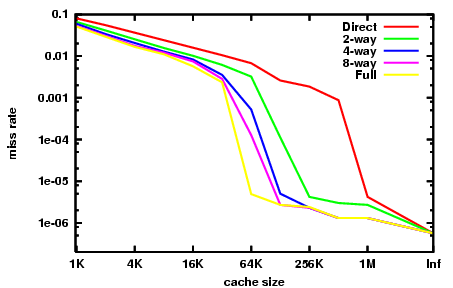
Cache size and miss rates — The larger a cache is, the less chance there will be of a conflict. — Again this means the miss rate decreases, so the AMAT and number of memory stall cycles also decrease. The complete Figure 7.29 depicts the miss rate as a function of both the cache size and its associativity.
What happens if the ratio of cache miss is more than cache hit in a system?
When a cache miss occurs, it takes up extra time and server resources which ends up slowing down your page speed load times. One cache miss isn’t a big deal, but the more that happens, the worse it is for your server’s resources, and page load times.
What causes high miss rate cache memory?
The more cache levels a system needs to check, the more time it takes to complete a request. This results in an increased cache miss rate, especially if the system needs to look into the main database to fetch the requested data.
Is 8 MB cache good?
So, 8MB doesn’t speed up all your data access all the time, but it creates (4 times) larger data “bursts” at high transfer rates. Benchmarking finds that these drives perform faster – regardless of identical specs.” “8mb cache is a slight improvement in a few very special cases.
Is more cache size better?
It’s safe to say that many processors would be much slower without it. The size of the cache is one of the most important factors in determining how fast your computer will be. All else being equal, a larger cache will mean faster processing speeds.
Is cache miss rate a good indicator of performance?
According to this article the cache-misses to instructions is a good indicator of cache performance. The ratio of cache-misses to instructions will give an indication how well the cache is working; the lower the ratio the better.
How do I choose a cache size?
Within these hard limits, the factors that determine appropriate cache size include the number of users working on the machine, the size of the files with which they usually work, and (for a memory cache) the number of processes that usually run on the machine.
Does cache affect performance?
Cache memory is a large determinant of system performance. The larger the cache, the more instructions can be queued and carried out. Storing instructions in cache reduces the amount of time it takes to access that instruction and pass it to a CPU core.
What is the cache miss rate?
Similarly, the miss rate is the number of total cache misses divided by the total number of memory requests made to the cache. One might also calculate the number of hits or misses on reads or writes only. Clearly, a higher hit rate will generally result in higher performance.
Is it dumb to say that more cores is better?
It’s a great goal which is worth spending money on, but it would be really “dumb” to simply say that “more cores is better”.
Why should I increase the number of cores in my CPU?
1 Applications that support multi-threading will greatly benefit from having a higher number of cores at their disposal 2 Increasing the amount of cores in your CPU is a cost effective way of increasing performance 3 Multi-threading support for applications will continue to improve over time More items…
What is the difference between miss rate and miss penalty?
The fraction or percentage of accesses that result in a miss is called the miss rate. The “extra” time required to fetch a block into a level of the memory hierarchy from the lower level is called miss penalty.
What is the difference between hit rate and miss rate?
The fraction or percentage of accesses that result in a hit is called the hit rate. The fraction or percentage of accesses that result in a miss is called the miss rate. The “extra” time required to fetch a block into a level of the memory hierarchy from the lower level is called miss penalty.