If you’re still getting errors relating to SSL security certificates on Chrome, disable your antivirus’ SSL or HTTPs scanning feature and try again. Go to the antivirus settings menu and disable HTTPS scanning or other features relating to internet security/protection.
Why HTTPS sites are not opening in Chrome?
Check your firewall/anti-virus software: Sometimes the settings of anti-virus software can treat certain HTTPS traffic as suspicious. To see if yours is interfering with accessing certain sites, you can either turn your firewall or anti-virus off completely, or (if it has this setting) turn off SSL scanning.
Why HTTPS sites are not opening?
You need to clear the SSL cache. You can do that from Internet Options page > Content tab. On that page, you will find an option called Clear SSL state. Click on it.
Why HTTPS sites are not opening in Chrome?
Check your firewall/anti-virus software: Sometimes the settings of anti-virus software can treat certain HTTPS traffic as suspicious. To see if yours is interfering with accessing certain sites, you can either turn your firewall or anti-virus off completely, or (if it has this setting) turn off SSL scanning.
Why HTTPS sites are not opening?
You need to clear the SSL cache. You can do that from Internet Options page > Content tab. On that page, you will find an option called Clear SSL state. Click on it.
Why is every website saying not secure?
The reason you are seeing the “Not Secure” warning is because the web page or website you are visiting is not providing an encrypted connection. When your Chrome browser connects to a website it can either use the HTTP (insecure) or HTTPS (secure).
Why is HTTPS crossed out?
Google Chrome crosses out the “https” in the URL of a site if the site has a security problem. Security issues can arise for a number of reasons, such as suspicious scripts or authentication problems.
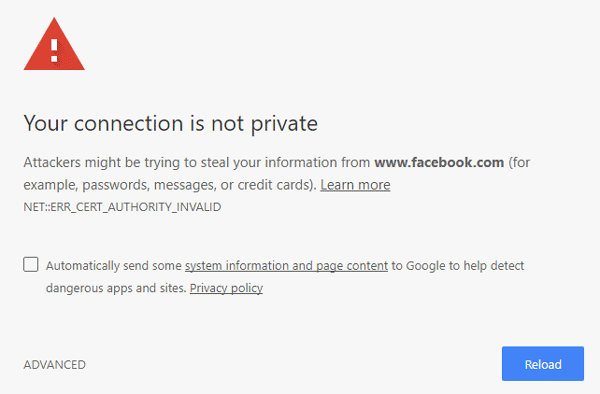
Why does Chrome keep saying your connection is not private?
A “your connection is not private” error means your browser cannot verify whether a website is safe to visit. Your browser issues this warning message to prevent you from visiting the site, because visiting an unsafe or unsecure site may put your personal information at risk.
Why is HTTPS crossed out?
Google Chrome crosses out the “https” in the URL of a site if the site has a security problem. Security issues can arise for a number of reasons, such as suspicious scripts or authentication problems.
Why HTTPS sites are not opening in Chrome?
Check your firewall/anti-virus software: Sometimes the settings of anti-virus software can treat certain HTTPS traffic as suspicious. To see if yours is interfering with accessing certain sites, you can either turn your firewall or anti-virus off completely, or (if it has this setting) turn off SSL scanning.
Why HTTPS sites are not opening?
You need to clear the SSL cache. You can do that from Internet Options page > Content tab. On that page, you will find an option called Clear SSL state. Click on it.
Google Chrome > Adding Trusted Sites Click on Settings, scroll to the bottom and click the Show Advanced Settings link. Click on Change proxy settings (under Network) Click the Security tab > Trusted Sites icon, then click Sites. Enter the URL of your Trusted Site, then click Add. Click Close > OK.
How do I know if HTTPS is enabled?
Verify HTTPS in your browser The quickest and easiest way to check if your website is using HTTPS is to visit your website from a web browser. In the address bar of that browser, you will either see a lock icon that is locked 🔒, or unlocked 🔓. Some browsers shows the lock at the end of the address.
What does red line through https mean?
You’re referring to when web browsers draw a red line through the “https://” in their URL bars. It means that the browser does not trust the certificate that the site is using, for many possible reasons: it isn’t signed by one of the root CA certificates that the browser implicitly trusts.
What is the https line called?
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (https) is a combination of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) with the Secure Socket Layer (SSL)/Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol.
How do you bypass your connection is not private on Google Chrome?
Process To The Website With An Insecure Connection To do so, click on the “Advanced” link. Click on the Advanced link to show “Proceed to website” link. And then hit on “Proceed to
Why does Chrome say not secure when certificate is valid?
When Chrome says a website is not secured, but the certificate is valid, that website may have mixed HTTPS and HTTP content. You can change the Internet connection settings to see if the problem is resolved. Another way to fix this issue is to clear the browser cache or contact the website administrator.
How do I know if HTTPS is enabled?
Verify HTTPS in your browser The quickest and easiest way to check if your website is using HTTPS is to visit your website from a web browser. In the address bar of that browser, you will either see a lock icon that is locked 🔒, or unlocked 🔓. Some browsers shows the lock at the end of the address.
How do I fix red line through https?
As a Web Surfer When you see the HTTPS part of a URL crossed out with a red line, the likeliest cause of the problem is with the website, not your browser. On the off chance that it is something cached in your browser, use your browser’s settings to clear the cookies and cached information and reload the site.
What does red line through https mean?
You’re referring to when web browsers draw a red line through the “https://” in their URL bars. It means that the browser does not trust the certificate that the site is using, for many possible reasons: it isn’t signed by one of the root CA certificates that the browser implicitly trusts.
Is HTTPS required by Google?
The new default for Google’s outlook on the internet includes encryption – a secure connection (HTTPS) is required, no longer a feature only for online banking and shopping sites.
How do I get HTTPS certificate?
To obtain an HTTPS certificate, perform the following steps: Create a private and public key pair, and prepare a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), including information about the organization and the public key. Contact a certification authority and request an HTTPS certificate, based on the CSR.