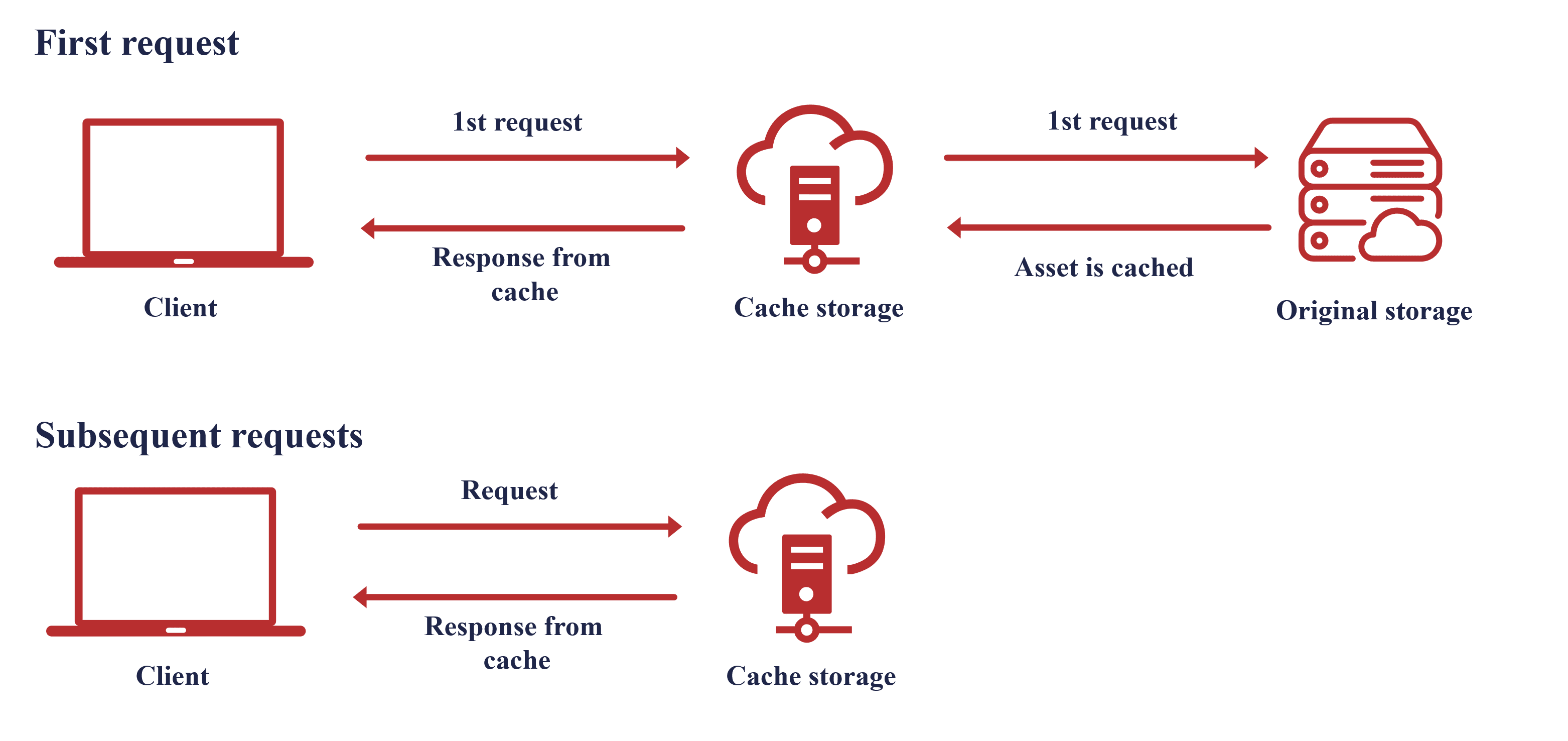
A cache hit occurs when an application or software requests data. First, the central processing unit (CPU) looks for the data in its closest memory location, which is usually the primary cache. If the requested data is found in the cache, it is considered a cache hit.A cache hit occurs when the requested data can be found in a cache, while a cache miss occurs when it cannot. Cache hits are served by reading data from the cache, which is faster than recomputing a result or reading from a slower data store; thus, the more requests that can be served from the cache, the faster the system performs.
How does cache hit work?
A cache hit describes the situation where your site’s content is successfully served from the cache. The tags are searched in the memory rapidly, and when the data is found and read, it’s considered as a cache hit. A cache hit is when content is successfully served from the cache instead of the server.
What is an example for a cache hit?
For example, if a CDN has 39 cache hits and 2 cache misses over a given timeframe, then the cache hit ratio is equal to 39 divided by 41, or 0.951. The cache hit ratio can also be expressed as a percentage by multiplying this result by 100. As a percentage, this would be a cache hit ratio of 95.1%.
How is cache hit rate calculated?
The best way to calculate a cache hit ratio is to divide the total number of cache hits by the sum of the total number of cache hits, and the number of cache misses. This value is usually presented in the percentage of the requests or hits to the applicable cache.
How do you know if a cache is a hit or miss?
If the desired data is in L1, then it’s a cache hit. And if the desired data is in another cache memory level then it’s a cache miss. An access that misses in L1 but hits in L2 wouldn’t usually be called a “cache miss”.
How does cache hit work?
A cache hit describes the situation where your site’s content is successfully served from the cache. The tags are searched in the memory rapidly, and when the data is found and read, it’s considered as a cache hit. A cache hit is when content is successfully served from the cache instead of the server.
How is cache hit rate calculated?
The best way to calculate a cache hit ratio is to divide the total number of cache hits by the sum of the total number of cache hits, and the number of cache misses. This value is usually presented in the percentage of the requests or hits to the applicable cache.
What can cause a cache miss?
A cache miss occurs either because the data was never placed in the cache, or because the data was removed (“evicted”) from the cache by either the caching system itself or an external application that specifically made that eviction request.
What is L1 L2 and L3 cache?
L2 and L3 caches are bigger than L1. They are extra caches built between the CPU and the RAM. Sometimes L2 is built into the CPU with L1. L2 and L3 caches take slightly longer to access than L1. The more L2 and L3 memory available, the faster a computer can run.
Where cache is stored?
In modern computers, the cache memory is stored between the processor and DRAM; this is called Level 2 cache. On the other hand, Level 1 cache is internal memory caches which are stored directly on the processor.
What is hit time in cache?
Two other terms used in cache performance measurement are the hit time—the time it takes to access a memory location in the cache and the miss penalty—the time it takes to load a cache line from main memory into cache.
Why a larger cache can increase the hit rate?
If you access many files and you have a large cache, you will have a larger cache-hit rate because older information still remains in the cache during consistency checks. However, if you have a small cache, there is less room for information to remain.
What means hit rate?
The percentage of the desired number of outcomes received by a salesperson relative to the total activity level. For example, it is the number of sales as a percentage of the number of calls. It also is called batting average and conversion rate.
How do I increase hit cache?
To increase your cache hit ratio, you can configure your origin to add a Cache-Control max-age directive to your objects, and specify the longest practical value for max-age .
Is it OK to clear cached data?
Clear out all cached app data These caches of data are essentially just junk files, and they can be safely deleted to free up storage space. Select the app you want, then the Storage tab and, finally the Clear Cache button to take out the trash.
Will clearing cache delete pictures?
The cache will be rebuild again unless you reduce the number of images on your device.
Is it okay to clear cache?
Clearing your cache on Android can free up valuable space and resolve issues with your phone’s battery, speed, and security. Old cached data can corrupt, causing larger performance problems. If a particular app receives an update, the cached data from a previous version can cause conflict.
How does cache invalidation work?
Cache invalidation describes the process of actively invalidating stale cache entries when data in the source of truth mutates. If a cache invalidation gets mishandled, it can indefinitely leave inconsistent values in the cache that are different from what’s in the source of truth.
How does cache hit work?
A cache hit describes the situation where your site’s content is successfully served from the cache. The tags are searched in the memory rapidly, and when the data is found and read, it’s considered as a cache hit. A cache hit is when content is successfully served from the cache instead of the server.
How is cache hit rate calculated?
The best way to calculate a cache hit ratio is to divide the total number of cache hits by the sum of the total number of cache hits, and the number of cache misses. This value is usually presented in the percentage of the requests or hits to the applicable cache.
How large is a cache line?
The cache line is generally fixed in size, typically ranging from 16 to 256 bytes. The effectiveness of the line size depends on the application, and cache circuits may be configurable to a different line size by the system designer.
Is cache a memory?
Computer cache definition Cache is the temporary memory officially termed “CPU cache memory.” This chip-based feature of your computer lets you access some information more quickly than if you access it from your computer’s main hard drive.
What is a cache hit and why is it important?
A cache hit describes the situation where your site’s content is successfully served from the cache. The tags are searched in the memory rapidly, and when the data is found and read, it’s considered as a cache hit. A cache hit is when content is successfully served from the cache instead of the server.
What is a cache hit in Seo?
The tags are searched in the memory rapidly, and when the data is found and read, it’s considered as a cache hit. A cache hit is when content is successfully served from the cache instead of the server. A cache hit can also be described as cold, warm, or hot.
What is the difference between Cache hits and cache miss?
If data is present it results in CACHE HITS, else CACHE MISS, i.e., data is not in cache memory so it retrieves data from main memory and inserts a block of data into the cache layer. The question that arises is: How many times machine will need to load a block into the cache layer, i.e. determine the number of CACHE MISS?
What is the purpose of a cache?
A cache’s primary purpose is to increase data retrieval performance by reducing the need to access the underlying slower storage layer. Trading off capacity for speed, a cache typically stores a subset of data transiently, in contrast to databases whose data is usually complete and durable.