The MySQL “Too many connections” error occurs when more queries are sent to a MySQL database than can be processed. The error can be fixed by setting a new number of maximum connections in the configuration file or globally.
How many connections MySQL can handle?
By default 151 is the maximum permitted number of simultaneous client connections in MySQL 5.5. If you reach the limit of max_connections you will get the “Too many connections” error when you to try to connect to your MySQL server. This means all available connections are in use by other clients.
How many SQL connections is too many?
By default, SQL Server allows a maximum of 32767 concurrent connections which is the maximum number of users that can simultaneously log in to the SQL server instance.
How do I check for too many connections in MySQL?
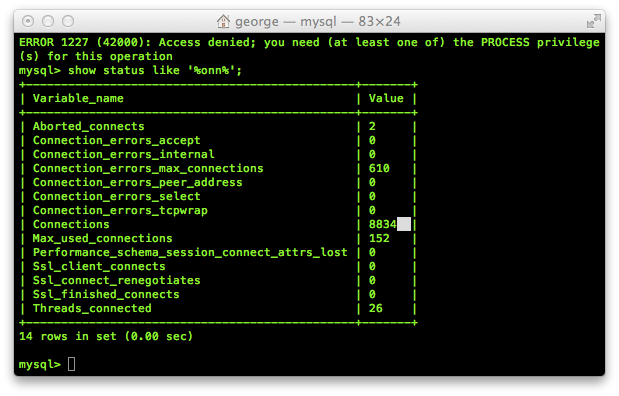
Information about connections to a server can be found using the SHOW STATUS statement: $ mysql –u root –p SHOW STATUS LIKE ‘max_used_connections’; First, you should ensure that your applications are closing connections to the server when they are no longer needed.
How many connections MySQL can handle?
By default 151 is the maximum permitted number of simultaneous client connections in MySQL 5.5. If you reach the limit of max_connections you will get the “Too many connections” error when you to try to connect to your MySQL server. This means all available connections are in use by other clients.
How do I check for too many connections in MySQL?
Information about connections to a server can be found using the SHOW STATUS statement: $ mysql –u root –p SHOW STATUS LIKE ‘max_used_connections’; First, you should ensure that your applications are closing connections to the server when they are no longer needed.
How do I fix too many connections error?
The MySQL “Too many connections” error occurs when more queries are sent to a MySQL database than can be processed. The error can be fixed by setting a new number of maximum connections in the configuration file or globally.
How long do MySQL connections last?
MySQL has its wait_timeout variable default value set to 28800 seconds (8 hours).
What happens when connection pool is full?
If the maximum pool size has been reached and no usable connection is available, the request is queued. The pooler then tries to reclaim any connections until the time-out is reached (the default is 15 seconds). If the pooler cannot satisfy the request before the connection times out, an exception is thrown.
What does it mean when a website says too many connections?
If you receive the “Too many connections” error message regularly, one of two things might be happening: Your site is experiencing consistently high traffic and your database is being overloaded with connection attempts. If this is the case, your site and your business may have outgrown shared web hosting.
How do I keep MySQL connection alive?
To prevent these connections being automatically closed, the connector can be configured to keep the connection alive by submitting a simple SELECT statement (actually SELECT ‘KEEP_ALIVE’;) periodically to ensure that the MySQL timeout is not reached and the connection closed.
How many connections can DB handle?
While theoretically, a database like SQL Server allows you to open 32,767 connections, in practice, a system resource bottleneck will emerge at a much lower value.
How do I find out how many active connections I have?
“netstat -a” shows all the currently active connections and the output display the protocol, source, and destination addresses along with the port numbers and the state of the connection.
How do I close all connections in a database?
How do I kill all database connections? Option 1: The Simple but Insufficient Approach: Offline the Database. Option 2: Dynamic SQL to Kill All User Sessions for the Database. Option 3: Alter the Database to SINGLE_USER or RESTRICTED_USER.
Why does MySQL keep losing connection?
The most common reason for the MySQL server has gone away error is that the server timed out and closed the connection. By default, the server closes the connection after 8 hours if nothing has happened. You can change the time limit by setting the wait_timeout variable when you start mysqld.
How do I change the max connection without restarting MySQL?
How do I close all connections in a database?
How do I kill all database connections? Option 1: The Simple but Insufficient Approach: Offline the Database. Option 2: Dynamic SQL to Kill All User Sessions for the Database. Option 3: Alter the Database to SINGLE_USER or RESTRICTED_USER.
How do I delete a MySQL connection?
In the Workbench, click the Connections icon ( ). The Connection Manager dialog box appears. Select an existing connection. Click Delete.
How many connections MySQL can handle?
By default 151 is the maximum permitted number of simultaneous client connections in MySQL 5.5. If you reach the limit of max_connections you will get the “Too many connections” error when you to try to connect to your MySQL server. This means all available connections are in use by other clients.
How do I check for too many connections in MySQL?
Information about connections to a server can be found using the SHOW STATUS statement: $ mysql –u root –p SHOW STATUS LIKE ‘max_used_connections’; First, you should ensure that your applications are closing connections to the server when they are no longer needed.
What causes a connection error?
Connection Errors. Connection errors can occur for a variety of reasons. For example, a failure in any of the internal connections described in How Connection Between the Application and DBMS Server Is Established results in a connection error. How connection errors are reported depends on where the failure occurs.
What happens if you don’t close MySQL connection?
If your script has a fair amount of processing to perform after fetching the result and has retrieved the full result set, you definitely should close the connection. If you don’t, there’s a chance the MySQL server will reach it’s connection limit when the web server is under heavy usage.