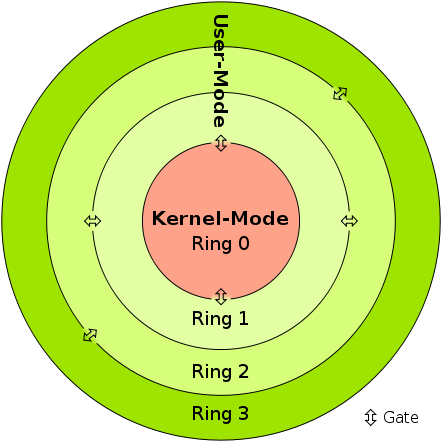
In kernel mode, the program has direct and unrestricted access to system resources. In user mode, the application program executes and starts. In user mode, a single process fails if an interrupt occurs. Kernel mode is also known as the master mode, privileged mode, or system mode.
What is the difference between kernel and user space?
Kernel space is strictly reserved for running a privileged operating system kernel, kernel extensions, and most device drivers. In contrast, user space is the memory area where application software and some drivers execute.
What is kernel mode in OS?
Kernel mode, also known as system mode, is one of the central processing unit (CPU) operating modes. While processes run in kernel mode, they have unrestricted access to the hardware. The other mode is user mode, which is a non-privileged mode for user programs.
What is the main difference between the user mode and kernel mode of operations for the modern operating systems give an example of an operation for each one of them?
The difference between User Mode and Kernel Mode is that user mode is the restricted mode in which the applications are running and kernel mode is the privileged mode which the computer enters when accessing hardware resources. The computer is switching between these two modes.
What is kernel mode in OS?
Kernel mode, also known as system mode, is one of the central processing unit (CPU) operating modes. While processes run in kernel mode, they have unrestricted access to the hardware. The other mode is user mode, which is a non-privileged mode for user programs.
Why kernel is high in memory?
On computers with a lot of physical memory, this can mean that there exists memory that the kernel cannot refer to directly—this is called high memory. When the kernel wishes to address high memory, it creates a mapping on the fly and destroys the mapping when done, which incurs a performance penalty.
Why is it called a kernel?
Definition It is the primary interface between the hardware and the processes of a computer. The kernel connects these two in order to adjust resources as effectively as possible. It is named a kernel because it operates inside the OS, just like a seed inside a hard shell.
What is kernel with example?
On most systems, the kernel is one of the first programs loaded on startup (after the bootloader). It handles the rest of startup as well as memory, peripherals, and input/output (I/O) requests from software, translating them into data-processing instructions for the central processing unit.
What is difference between kernel & OS?
Operating System is a system software. Kernel is system software which is part of operating system. Operating System provides interface between user and hardware. Kernel provides interface between applications and hardware.
What are the 2 modes of the operating system?
There are two modes of operation in the operating system to make sure it works correctly. These are user mode and kernel mode.
What is deadlock OS?
A deadlock is a situation in which two computer programs sharing the same resource are effectively preventing each other from accessing the resource, resulting in both programs ceasing to function. The earliest computer operating systems ran only one program at a time.
What is kernel used for?
It is the core that provides basic services for all other parts of the OS. It is the main layer between the OS and underlying computer hardware, and it helps with tasks such as process and memory management, file systems, device control and networking.
Why do we need two modes in OS?
The dual-mode operations in the operating system protect the operating system from illegal users. We accomplish this defense by designating some of the system instructions as privileged instructions that can cause harm. The hardware only allows for the execution of privileged instructions in kernel mode.
Why are two modes user and kernel mode needed?
Why are two modes (user and kernel) needed? User mode prohibits the user from accessing certain areas of memory and executing certain instructions to protect the OS. Kernel mode gives full access to the OS to allow it to do what it needs to do.
Why kernel mode is more sensitive than user mode?
The reason for this is because if all programs ran in kernel mode, they would be able to overwrite each other’s memory. If it needs to access any of these features – it makes a call to the underlying API. Each process started by windows except of system process runs in user mode.
What happens in user space and kernel space?
A user space process is executed by a user in the operating system, rather than being part of the operating system itself. It might also be executed by an init system (e.g. systemd), but it isn’t part of the kernel. User space is the area of memory that non-kernel applications run in.
What is user space in Linux?
User space refers to all of the code in an operating system that lives outside of the kernel. Most Unix-like operating systems (including Linux) come pre-packaged with all kinds of utilities, programming languages, and graphical tools – these are user space applications. We often refer to this as “userland.”
Can kernel access user space memory?
Whilst a user-space program is not allowed to access kernel memory, it is possible for the kernel to access user memory. However, the kernel must never execute user-space memory and it must also never access user-space memory without explicit expectation to do so.
What is kernel mode in OS?
Kernel mode, also known as system mode, is one of the central processing unit (CPU) operating modes. While processes run in kernel mode, they have unrestricted access to the hardware. The other mode is user mode, which is a non-privileged mode for user programs.
What is the main difference between the user mode and kernel mode of operations for the modern operating systems give an example of an operation for each one of them?
The difference between User Mode and Kernel Mode is that user mode is the restricted mode in which the applications are running and kernel mode is the privileged mode which the computer enters when accessing hardware resources. The computer is switching between these two modes.
How many kernels are in OS?
Kernels are of five types, namely monolithic, microkernel, nanokernel, hybrid kernel and exokernel. Functions of a kernel include scheduling processes, resource allocation, device management, interrupt handling, memory management, and process management.
What is kernel in simple words?
The kernel is a core component of an operating system and serves as the main interface between the computer’s physical hardware and the processes running on it. The kernel enables multiple applications to share hardware resources by providing access to CPU, memory, disk I/O, and networking.