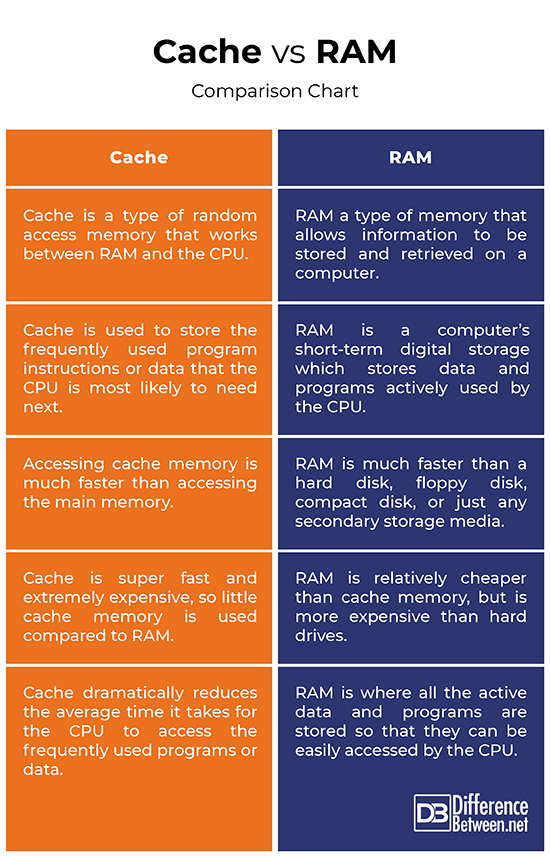
1. RAM is a volatile memory that could store the data as long as the power is supplied. Cache is a smaller and fast memory component in the computer.
Is cache memory part of RAM?
The RAM that is used for the temporary storage is known as the cache. Since accessing RAM is significantly faster than accessing other media like hard disk drives or networks, caching helps applications run faster due to faster access to data.
What are the main differences between the cache memory inside the CPU and RAM?
Both cache and RAM are volatile memory. The difference between cache and RAM is that the cache is a fast memory component that stores the frequently used data by the CPU while RAM is a computing device that stores data and programs currently used by the CPU. In brief, the cache is faster and expensive than RAM.
Which one is faster RAM or cache?
Since the cache memory is faster than RAM, and because it is located closer to the CPU, it can get and start processing the instructions and data much more quickly. The same procedure is carried out when data or instructions need to be written back to memory.
Where is cache stored?
The data in a cache is generally stored in fast access hardware such as RAM (Random-access memory) and may also be used in correlation with a software component. A cache’s primary purpose is to increase data retrieval performance by reducing the need to access the underlying slower storage layer.
Why is cache memory used?
Cache memory is used to reduce the average time to access data from the Main memory. The cache is a smaller and faster memory which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations.
What type of memory is cache?
The cache augments, and is an extension of, a computer’s main memory. Both main memory and cache are internal random-access memories (RAMs) that use semiconductor-based transistor circuits. Cache holds a copy of only the most frequently used information or program codes stored in the main memory.
Is cache memory a form of ROM?
Cache memory is a form of ROM. Level 1 cache usually contains the least amount of storage of the cache memory levels. Accessing data from the hard drive to send to the CPU is faster than accessing data from RAM. The heads of a hard disk drive touch the surface of the platter to read or write the data.
Where is cache stored?
The data in a cache is generally stored in fast access hardware such as RAM (Random-access memory) and may also be used in correlation with a software component. A cache’s primary purpose is to increase data retrieval performance by reducing the need to access the underlying slower storage layer.
What is cache memory example?
Memory cache – When an application is running, it may cache certain data in the system memory, or RAM. For example, if you are working on a video project, the video editor may load specific video clips and audio tracks from the hard drive into RAM.
What is cache memory in simple words?
Cache is the temporary memory officially termed “CPU cache memory.” This chip-based feature of your computer lets you access some information more quickly than if you access it from your computer’s main hard drive.
How much cache memory is good for laptop?
It’s hard to say how much processor cache you need, but 3-6MB is typical in current laptops and PCs. But given the performance benefits, more cache and a slower clock speed is likely to be faster than the opposite.
Is cache smaller than RAM?
Since cache memory is much smaller than server RAM, the data it stores is only temporary, and so it may not hold the information that the processor needs. When the cache does not have the processor’s required data, this is called a cache miss, and in this instance the CPU will move onto the hard drive and use RAM.
Can cache data be deleted?
Android works in the same way as iPhone when it comes to deleting cached data. You’ll need to specifically find an app under your settings to delete the cached data.
Does clearing cache delete data?
Clearing cache is a quick and easy way to free up space and (hopefully) fix a misbehaving app. Clearing app cache will not delete app data like account information.
What is the purpose of RAM?
RAM (Random Access Memory) is the hardware in a computing device where the operating system (OS), application programs and data in current use are kept so they can be quickly reached by the device’s processor. RAM is the main memory in a computer.
What is cache memory types?
There are two different types of cache memory: primary and secondary. Primary cache memory is found on the CPU itself whereas secondary cache memory is found on a separate chip close to the CPU. Although, as time has progressed, the secondary cache has become rather obsolete as most caches are found on the CPU.
How does cache work?
How Does Caching Work? Cached data works by storing data for re-access in a device’s memory. The data is stored high up in a computer’s memory just below the central processing unit (CPU).
Why is cache memory used?
Cache memory is used to reduce the average time to access data from the Main memory. The cache is a smaller and faster memory which stores copies of the data from frequently used main memory locations. There are various different independent caches in a CPU, which store instructions and data.
What is the maximum size of cache memory?
The maximum theoretical cache size is 2 GB. The size of cache you can specify is limited by the amount of physical memory and paging space available to the system. The shared class cache consists of memory mapped files that are created on disk and remain when the operating system is restarted.
What’s the function of cache?
Caches are used to store temporary files, using hardware and software components. An example of a hardware cache is a CPU cache. This is a small chunk of memory on the computer’s processor used to store basic computer instructions that were recently used or are frequently used.
Is cache smaller than RAM?
Since cache memory is much smaller than server RAM, the data it stores is only temporary, and so it may not hold the information that the processor needs. When the cache does not have the processor’s required data, this is called a cache miss, and in this instance the CPU will move onto the hard drive and use RAM.