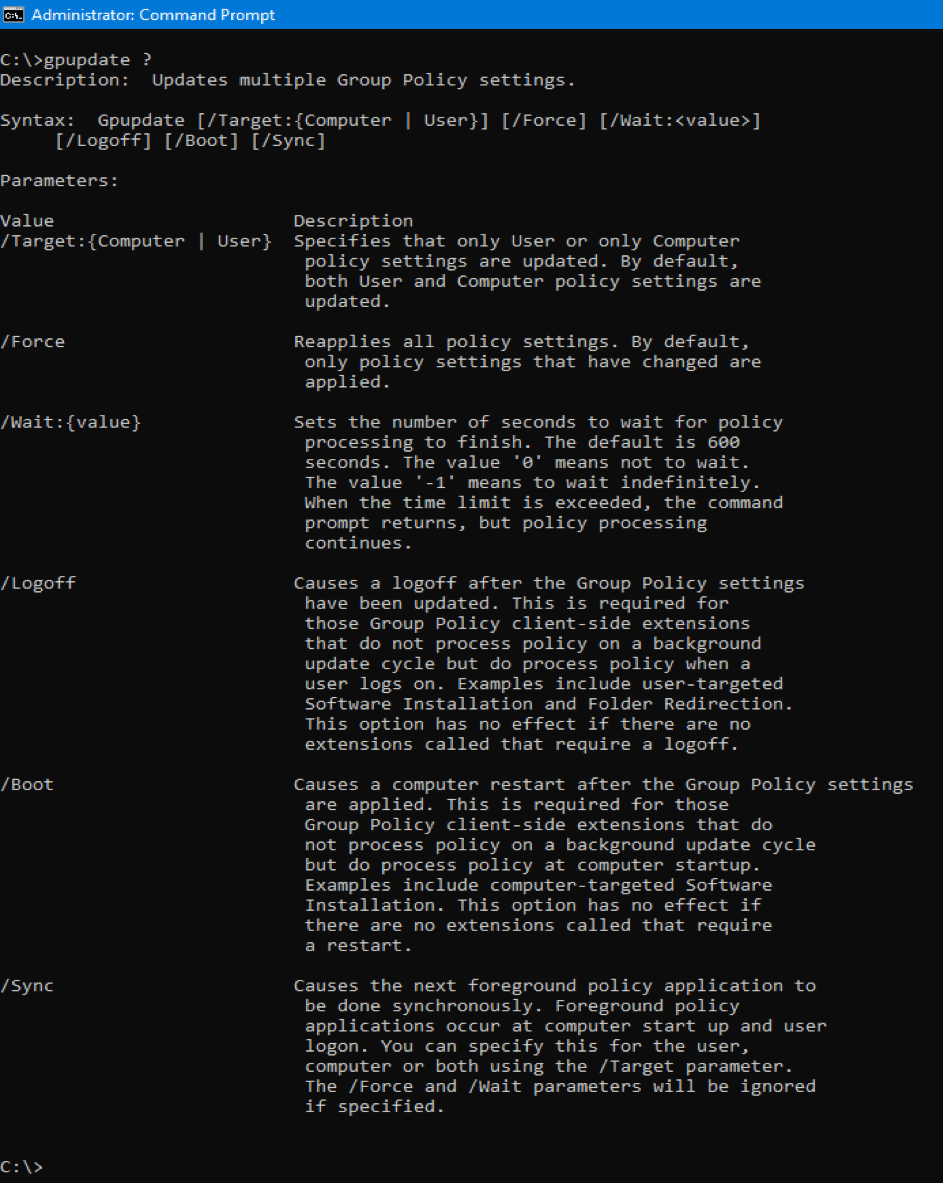
GPupdate – Applies only policies that have changed. For example, you update the policy that enabled the windows lock screen. This command will only apply that one policy that changed. GPUpdate /force – This command reapplies all policy settings.
What is Gpupdate force?
The gpupdate command refreshes a computer’s local Group Policy, and any Active Directory-based group policies.
What is the difference between Gpupdate force and Gpupdate sync?
What is the Difference Between GPUpdate and GPUpdate /force? The gpupdate command applies only changed policies, and the GPUpdate /force command reapplies all client policies—both new and old (regardless of whether they have been changed). In most cases, you need to use gpupdate to update the policies on the computer.
Is Gpupdate force necessary?
Contrary to popular belief, you don’t actually need it unless under certain circumstances. By default, gpupdate is smart; it compares all current settings with any new settings and only applies them. But, you can also force gupdate to reapply all settings using the /force switch.
What is the difference between Gpupdate and Gpresult commands?
– gpupdate [/target: {computer/user}] [/force] [ /wait: value] [/logoff] [/boot]. The gpresult command displays Group Policy settings and Resultant Set of Policy (RSOP) for a user or a computer. – /s computer specifies the name or IP address of a remote computer. (Do not use backslashes.)
What is the difference between Gpupdate force and Gpupdate sync?
What is the Difference Between GPUpdate and GPUpdate /force? The gpupdate command applies only changed policies, and the GPUpdate /force command reapplies all client policies—both new and old (regardless of whether they have been changed). In most cases, you need to use gpupdate to update the policies on the computer.
Is Gpupdate force necessary?
Contrary to popular belief, you don’t actually need it unless under certain circumstances. By default, gpupdate is smart; it compares all current settings with any new settings and only applies them. But, you can also force gupdate to reapply all settings using the /force switch.
How often is Gpupdate run?
By default, Windows will update group policy settings every 90 minutes or when during a computer reboot. There are times when you need to immediately update a computer’s policies and waiting 90 minutes is not an option. By using the gpupdate command you can force a policy update.
What is Gpresult command?
The gpresult command displays the resulting set of policy settings that were enforced on the computer for the specified user when the user logged on. Because /v and /z produce a lot of information, it’s useful to redirect output to a text file (for example, gpresult/z >policy.
Can you run Gpupdate remotely?
What is the use of Group Policy?
Group Policy is an infrastructure that allows you to specify managed configurations for users and computers through Group Policy settings and Group Policy Preferences. To configure Group Policy settings that affect only a local computer or user, you can use the Local Group Policy Editor.
Is restart required after Gpupdate?
Sometimes you will not be presented with a prompt to restart or logoff after the update. However, you should still restart your computer unless otherwise instructed by IT.
What is the difference between RsoP and GPResult?
GPResult is a command line tool that shows the Resultant Set of Policy (RsoP) information for a user and computer. In other words, it creates a report that displays what group policy objects are applied to a user and computer.
How do I use Gpupdate at Target?
In the Command Prompt window, type gpupdate /target: computer and press Enter to update only those computer policies that have been changed. To update all computer policies, in place of the previous command, type gpupdate /target: computer /force and press Enter.
Do I need to restart after Gpupdate?
It’s best to completely restart the computer, and it is slightly faster to reboot manually than to reboot through the Command Line window. Sometimes you will not be presented with a prompt to restart or logoff after the update. However, you should still restart your computer unless otherwise instructed by IT.
What does Group Policy do?
Group Policy is an infrastructure that allows you to specify managed configurations for users and computers through Group Policy settings and Group Policy Preferences. To configure Group Policy settings that affect only a local computer or user, you can use the Local Group Policy Editor.
How do I check my Gpupdate results?
Open a command prompt window, type gpresult, and hit Enter to see the parameter list. Now from the available parameters, if you use the command gpresult /Scope Computer /v you will be able to see all the policies that have been applied to your computer.
Why does group policy take so long?
Actually, there are a number of reasons why Group Policies take a long time to be applied: these can be DNS issues, DC availability and the speed of connection to it, wrong configuration of AD sites or replication problems, misconfigured group policies, incorrect scripts, etc.
What is the difference between Gpupdate force and Gpupdate sync?
What is the Difference Between GPUpdate and GPUpdate /force? The gpupdate command applies only changed policies, and the GPUpdate /force command reapplies all client policies—both new and old (regardless of whether they have been changed). In most cases, you need to use gpupdate to update the policies on the computer.
Is Gpupdate force necessary?
Contrary to popular belief, you don’t actually need it unless under certain circumstances. By default, gpupdate is smart; it compares all current settings with any new settings and only applies them. But, you can also force gupdate to reapply all settings using the /force switch.
How do I enable Group Policy?
Open the Local Group Policy Editor and then go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Control Panel. Double-click the Settings Page Visibility policy and then select Enabled.
What is GPO command?
Description. The Get-GPO cmdlet gets one Group Policy Object (GPO) or all the GPOs in a domain. You can specify a GPO by its display name or by its globally unique identifier (GUID) to get a single GPO, or you can get all the GPOs in the domain through the All parameter.