You can also access the Troubleshooters via Windows Settings. Press Win+I to open Settings > Update & security > Troubleshoot. Here you will see all the Troubleshooters. More on this at – Run Troubleshooters using the Troubleshoot page.
What is the command for Windows troubleshooting command?
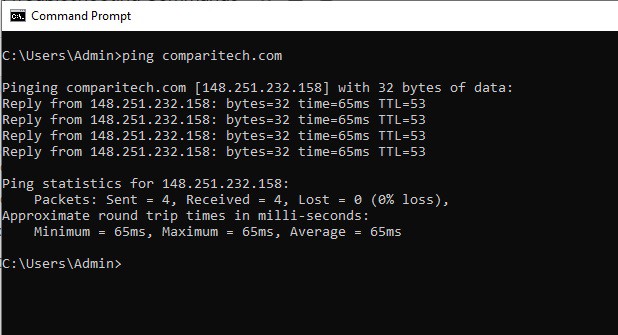
The IPConfig command is one of the more useful basic Windows network commands everyone should know and use to troubleshoot problems. The IPConfig command displays basic IP address configuration information for the Windows device you are working on.
How do I run Windows Troubleshooter?
To run a troubleshooter: Select Start > Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot, or select the Find troubleshooters shortcut at the end of this topic. Select the type of troubleshooting you want to do, then select Run the troubleshooter. Allow the troubleshooter to run and then answer any questions on the screen.
What is the command for Windows troubleshooting command?
The IPConfig command is one of the more useful basic Windows network commands everyone should know and use to troubleshoot problems. The IPConfig command displays basic IP address configuration information for the Windows device you are working on.
How do I run Windows Troubleshooter on Windows 11?
Run troubleshooter in Windows 11 Tap the Win+I keyboard shortcut to open the Settings app. Go to System. Scroll all the way down and select Troubleshoot. Click Other Troubleshooters.
Why can’t I run troubleshooter Windows 10?
If you are getting “Troubleshooter has stopped working” error messages, the problem might lie with your group policy settings. Press Win + R and type in gpedit. msc . Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Troubleshooting and Diagnostics > Scripted Diagnostics.
What does dism Scanhealth do?
When you use the /CheckHealth sfc argument, the DISM tool will report whether the image is healthy, repairable, or non-repairable. If the image is non-repairable, you should discard the image and start again. If the image is repairable, you can use the /RestoreHealth argument to repair the image.
What is netsh command?
Netsh is a command-line scripting utility that allows you to display or modify the network configuration of a computer that is currently running. Netsh commands can be run by typing commands at the netsh prompt and they can be used in batch files or scripts.
What are the 3 main commands in IP config?
IPCONFIG /release [adapter] Release the IP address for the specified adapter. IPCONFIG /renew [adapter] Renew the IP address for the specified adapter. IPCONFIG /flushdns Purge the DNS Resolver cache.
What is the command for Windows troubleshooting command?
The IPConfig command is one of the more useful basic Windows network commands everyone should know and use to troubleshoot problems. The IPConfig command displays basic IP address configuration information for the Windows device you are working on.
What is the Command Prompt for advanced troubleshooting?
#2: Access command prompt from the recovery environment. In Windows 10/11, click Start > Settings > Update & Security > Recovery > Advanced startup and then Restart now to boot into recovery environment. And then, click Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt or directly press Shift + F10 to summon it.
What is a DISM command?
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) is a command-line tool that is used to service Windows images. You can use DISM image management commands to mount and get information about Windows image (. wim) files, Full-flash utility (FFU) files, or virtual hard disks (VHD).
How do I run DISM?
Open Start. Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option. Type the following command to perform an advanced DISM scan and press Enter: DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth.
Should I run DISM or SFC first?
SFC will scan the integrity of all protected operating system files, including those that are not on your hard drive. It should be used before running DISM.
How do you do automatic repairs?
In the command prompt window, type “chkdsk /r c:” and hit Enter. This command will check your drive for errors using the CHKDSK utility and automatically repair them if possible. Type “sfc /scannow” and hit Enter. This will check the integrity of Windows system files using the System File Checker tool.
How do I fix disk errors using command prompt?
To repair errors without scanning the disk for bad sectors, at the command prompt, type chkdsk volume: /f, and then press
Can I run chkdsk in Windows 10?
Generally, CHKDSK is run via Command Prompt in Windows 10 (or Windows 8 and 7). Using unique commands like chkdsk /f or chkdsk /r, you can scan your Windows file system — NTFS (New Technology File System) on Windows XP or later — to pinpoint data errors on your drive and fix them.
How do you fix disk problems?
To fix disk errors, you can use the Chkdsk tool found in Windows operating systems. Chkdsk (Chkdsk.exe) is a command-line tool that creates and displays a status report for the disk by checking volumes for problems.
Does Windows 11 have a repair tool?
If your Windows 11 computer won’t start properly, it may boot into the Startup Repair interface. Then, you can use Startup Repair to repair Windows 11. This tool can scan your computer for issues like missing and damaged system files.
How do I troubleshoot Windows 10 without Settings?
To gain access to this, go to the Start Menu > Power Icon > and then hold down Shift whilst clicking the Restart option. You can then, go to Troubleshoot > Reset this PC > Keep my files to do what you ask.
How do I manually run Windows Update Troubleshooter?
If you get an error code while downloading and installing Windows updates, the Update Troubleshooter can help resolve the problem. Select Start > Settings > System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters.
How do you get to command prompt?
The quickest way to open a Command Prompt window is through the Power User Menu, which you can access by right-clicking the Windows icon in the bottom-left corner of your screen, or with the keyboard shortcut Windows Key + X. It’ll appear in the menu twice: Command Prompt and Command Prompt (Admin).