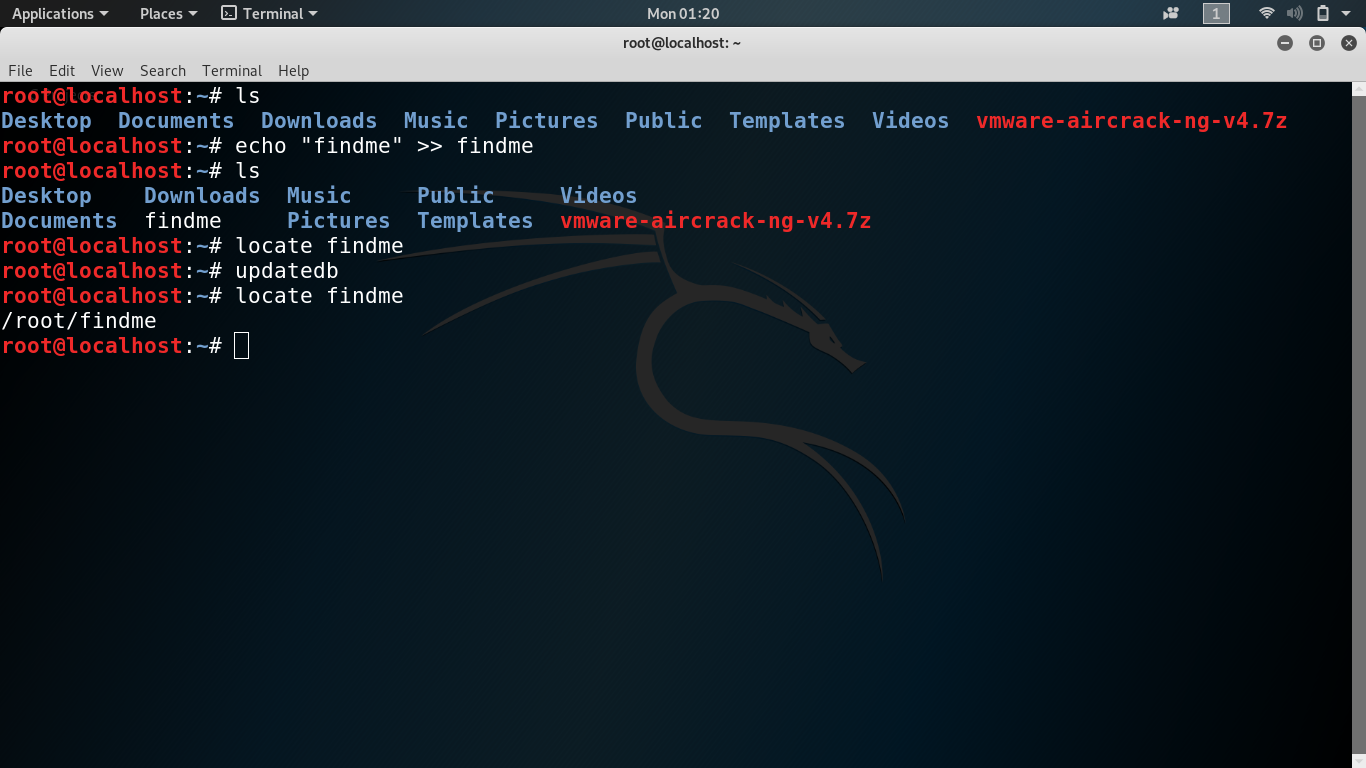
locate is a Unix utility which serves to find files on filesystems. It searches through a prebuilt database of files generated by the updatedb command or by a daemon and compressed using incremental encoding. It operates significantly faster than find , but requires regular updating of the database.
What is locate used for?
The locate command is a Unix utility used for quickly finding files and directories. The command is a more convenient and efficient alternative to the find command, which is more aggressive and takes longer to complete the search.
Where is locate database?
The default database that locate utility reads is /var/lib/mlocate/mlocate. db, but if you wish to link the locate command with some other database kept at some other location, use the -d option.
How do I find the locate command?
To check whether the locate utility is installed, open up your terminal, type locate and press Enter . If the package is installed, the system will display locate: no pattern to search for specified . Otherwise, you will see something like locate command not found .
What is Updatedb?
updatedb creates and updates the database of file names used by locate . updatedb generates a list of files similar to the output of find and then uses utilities for optimizing the database for performance. updatedb is often run periodically as a cron job and configured with environment variables or command options.
What is locate used for?
The locate command is a Unix utility used for quickly finding files and directories. The command is a more convenient and efficient alternative to the find command, which is more aggressive and takes longer to complete the search.
How do I find the locate command?
To check whether the locate utility is installed, open up your terminal, type locate and press Enter . If the package is installed, the system will display locate: no pattern to search for specified . Otherwise, you will see something like locate command not found .
Which is faster find or locate?
The reason locate is faster than find is because it relies on a database that lists all the files on the filesystem. This database is usually updated once a day with a cron script, but you can update it manually with the updatedb command.
Is locate and find the same?
Although both commands have the same function, they work differently. The find command will search for the specified files in all of your computer’s directories. Meanwhile, the locate command will look for files only on your Linux database.
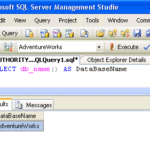
Where is located SQL Server?
Where SQL database is stored?
SQL Server databases are stored in the file system in files. Files can be grouped into filegroups. For more information about files and filegroups, see Database Files and Filegroups. When people gain access to an instance of SQL Server they are identified as a login.
Is there a locate command in Windows?
The short answer is that there is no exact equivalent on Windows. The workaround is to use the dir command. This is a directory list command that supports special characters, and can be used as pointed out in the accepted answer. The Locate command on many Unix like systems is an index based search.
What is difference between find and locate CMD?
Locate searches for files from a database that is created automatically. This database contains the list of files in a file system and their associated paths. So essentially locate simply searches through a file and returns a match. Find on the other hand searches through files in the file system in real time.
Why locate is not working?
If you encounter the error locate command not found on your Linux system, it likely means that you do not have the software installed and therefore can’t use this command.
How often does Updatedb Run?
updatedb is usually run daily by cron(8) to update the default database.
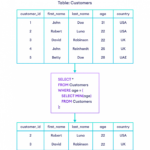
What is locate in SQL?
The LOCATE() function returns the position of the first occurrence of a substring in a string. If the substring is not found within the original string, this function returns 0. This function performs a case-insensitive search. Note: This function is equal to the POSITION() function.
What are the advantages using locate over find?
locate uses a prebuilt database, which should be regularly updated, while find iterates over a filesystem to locate files. Thus, locate is much faster than find , but can be inaccurate if the database -can be seen as a cache- is not updated (see updatedb command).
How do I use locate in Delphi?
Locate moves the cursor to the first row matching a specified set of search criteria. In its simplest form, you pass Locate the name of a column to search, a field value to match, and an options flag specifying whether the search is case-insensitive or if it can use partial-key matching.
What is difference between find and locate commands?
locate simply looks its database and reports the file location. find does not use a database, it traverses all the directories and their sub directories and looks for files matching the given criterion.
What is locate used for?
The locate command is a Unix utility used for quickly finding files and directories. The command is a more convenient and efficient alternative to the find command, which is more aggressive and takes longer to complete the search.
How do I find the locate command?
To check whether the locate utility is installed, open up your terminal, type locate and press Enter . If the package is installed, the system will display locate: no pattern to search for specified . Otherwise, you will see something like locate command not found .
What are the advantages using locate over find?
locate uses a prebuilt database, which should be regularly updated, while find iterates over a filesystem to locate files. Thus, locate is much faster than find , but can be inaccurate if the database -can be seen as a cache- is not updated (see updatedb command).