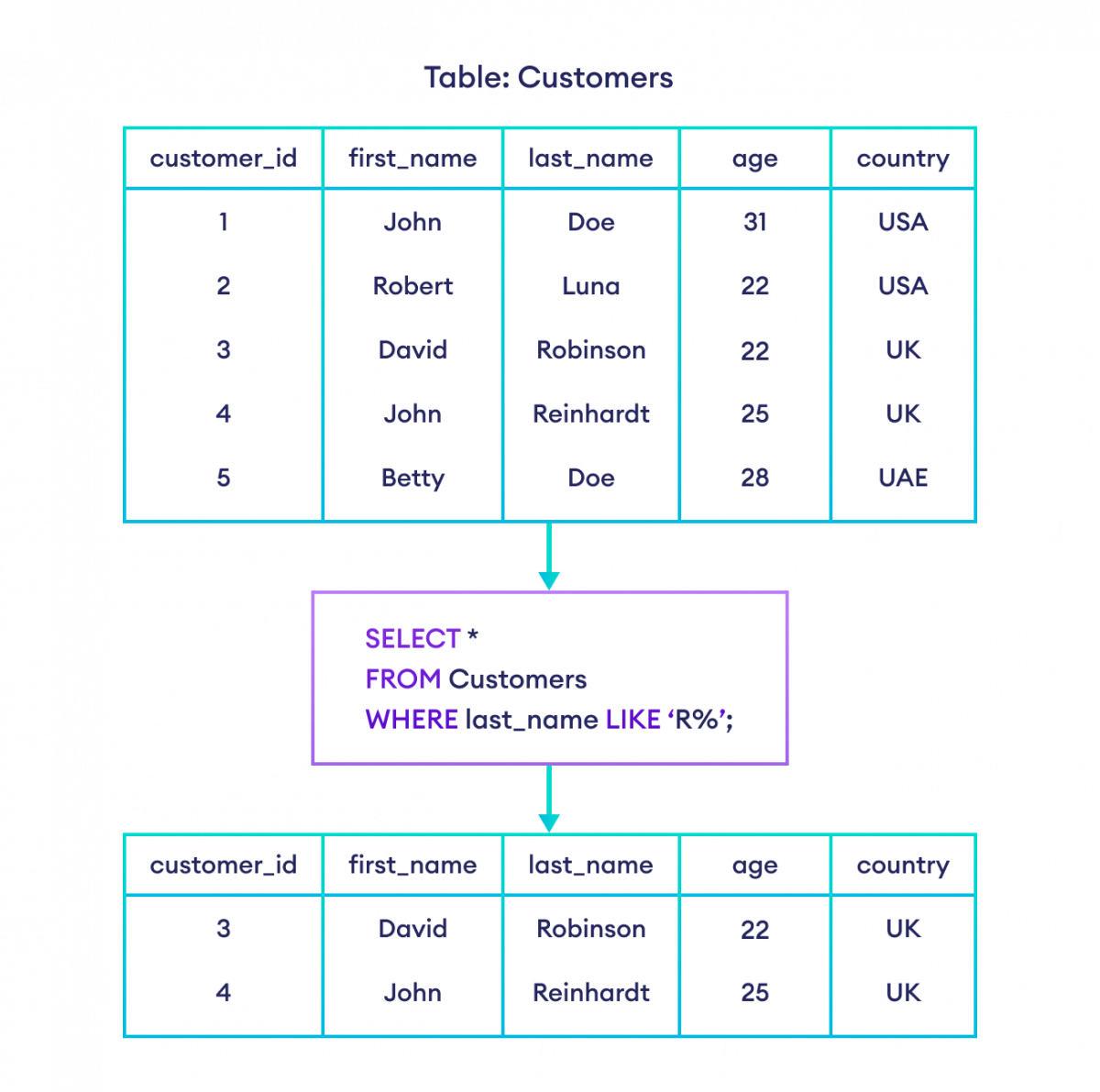
A wildcard character is used to substitute one or more characters in a string. Wildcard characters are used with the LIKE operator. The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column.
What does the * wildcard mean in SQL?
A wildcard character is used to substitute one or more characters in a string. Wildcard characters are used with the LIKE operator. The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column.
What does the * wildcard mean in SQL?
A wildcard character is used to substitute one or more characters in a string. Wildcard characters are used with the LIKE operator. The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column.
Should you use * in SQL?
That’s all about why you should not use SELECT * in the SQL query anymore. It’s always better to use the explicit column list in the SELECT query than a * wildcard. It not only improves the performance but also makes your code more explicit.
What is difference between * and & wildcard character?
Difference between wildcards (*) and (?) A wildcard character is a kind of placeholder represented by a single character, such as an asterisk (*) and question mark (?), which can be interpreted as a number of literal characters or an empty string.
What is the difference between * and wildcard characters?
Alternatively referred to as a wild character or wildcard character, a wildcard is a symbol used to replace or represent one or more characters. The most common wildcards are the asterisk (*), which represents one or more characters, and question mark (?), which represents a single character.
What does the wildcard operator * do?
The asterisk ( * ) The asterisk represents any number of unknown characters. Use it when searching for documents or files for which you have only partial names. For most web search engines, wildcards increase the number of your search results.
What does an asterisk (*) mean in your code in SQL?
The asterisk or star symbol ( * ) means all columns. The semi-colon ( ; ) terminates the statement like a period in sentence or question mark in a question.
What is the purpose of * In wildcard selector?
The * wildcard is known as the containing wildcard since it selects elements containing the set value. With the ^ wildcard, you get to select elements whose attribute value starts with the set value. The $ wildcard lets you select elements whose attribute values end with the specified value.
What is difference between * and & wildcard character?
Difference between wildcards (*) and (?) A wildcard character is a kind of placeholder represented by a single character, such as an asterisk (*) and question mark (?), which can be interpreted as a number of literal characters or an empty string.
What does the * wildcard mean in SQL?
A wildcard character is used to substitute one or more characters in a string. Wildcard characters are used with the LIKE operator. The LIKE operator is used in a WHERE clause to search for a specified pattern in a column.
Why select * is not good?
When you SELECT *, you’re often retrieving more columns from the database than your application really needs to function. This causes more data to move from the database server to the client, slowing access and increasing load on your machines, as well as taking more time to travel across the network.
Is select * a good practice?
If you are writing application code, then select * is a poor practice. You want the application to be specific about the columns it is using. And you don’t want to return unnecessary data to the application.
Should you use select * in code?
Avoid using SELECT * When writing queries, it would be better to set the columns you need in the select statement rather than SELECT *. There are many reasons for that recommendation, like: SELECT * Retrieves unnecessary data besides that it may increase the network traffic used for your queries.
Is SELECT * SELECT all same?
SELECT ALL means ALL rows, i.e including duplicate rows. (The opposite is SELECT DISTINCT , where duplicate rows are removed.) ALL is the default, and most people write just SELECT instead of SELECT ALL . SELECT * means all columns.
What is asterisk called in SQL?
The asterisk or star symbol ( * ) means all columns. The semi-colon ( ; ) terminates the statement like a period in sentence or question mark in a question.
Which 2 wildcards are used in SQL?
To broaden the selections of a structured query language (SQL-SELECT) statement, two wildcard characters, the percent sign (%) and the underscore (_), can be used.
What does a * do in SQL?
You can obviously retrieve multiple columns for each record, and (only if you want to retrieve all the columns) you can replace the list of them with * , which means “all columns”. So, in a SELECT statement, writing * is the same of listing all the columns the entity has.
Why is an asterisk (*) used here?
It is most commonly used to signal a footnote, but it is sometimes also used to clarify a statement or to censor inappropriate language.
How * is called?
* is called an asterisk; although sometimes people will use the generic term “star.” When it is used in mathematical equations, people say “times.” Example 12*2=24 would be read out loud as: Twelve times two equals twenty-four.
Is SELECT * faster than SELECT column?
Selecting distinct and less than all columns will always be faster than selecting *.
Can we use SELECT * with group by?
You can use a SELECT command with a GROUP BY clause to group all rows that have identical values in a specified column or combination of columns, into a single row.