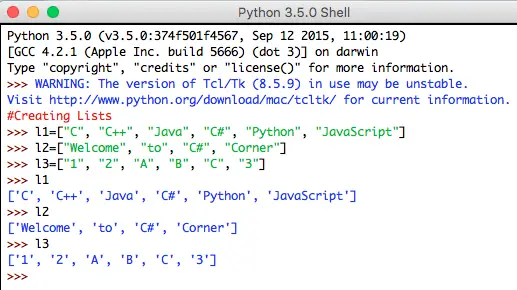
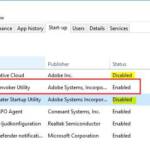
The correct syntax to create a Python List is using the square brackets. Creating a list is as simple as putting different comma-separated values between square brackets. Through this, using Lists you can store multiple items. A list can have integer, string or float elements.
What is a syntax in Python example?
The syntax of the Python programming language is the set of rules which defines how a Python program will be written. Python Line Structure: A Python program is divided into a number of logical lines and every logical line is terminated by the token NEWLINE. A logical line is created from one or more physical lines.
What is basic syntax of Python?
Syntax is one of the basic requirements that we must know to code in any language. In Python, we use indentation to represent the block of the code. We have to follow some rules about how to use the indentation. Not just indentation, we have to follow the rules on how to choose the name for the variables.
What is a list of lists in Python?
A list of lists is a list where each element is a list by itself. The List is one of the 4 built-in data types in Python. One can learn more about other Python data types here.
What is basic syntax?
What Is Basic Syntax? Basic syntax represents the fundamental rules of a programming language. Without these rules, it is impossible to write functioning code. Every language has its own set of rules that make up its basic syntax.
What Is syntax in a code?
Syntax is the set of rules that define what the various combinations of symbols mean. This tells the computer how to read the code. Syntax refers to a concept in writing code dealing with a very specific set of words and a very specific order to those words when we give the computer instructions.
Why is syntax important in Python?
The Python syntax defines all the set of rules that are used to create sentences in Python programming. For example – We have to learn grammar to learn the English language. In the same way, you will need to learn and understand the Python syntax in order to learn the Python language.
Why is Python syntax easy?
Because Python is similar to English, many find it easier to learn than other programming languages. Developers can read and remember the Python syntaxes much easier than other programming languages. Since Python supports scripting as well, it can be used to build large, commercial applications.
What is the syntax of a Python class?
A class in Python can be defined using the class keyword. As per the syntax above, a class is defined using the class keyword followed by the class name and : operator after the class name, which allows you to continue in the next indented line to define class members.
What does list () mean?
The list() function creates a list object. A list object is a collection which is ordered and changeable. Read more about list in the chapter: Python Lists.
Why is it called a list in Python?
They’re named after the list abstract data type, not linked lists. This is similar to the naming of Java’s List interface and C#’s List
What are lists and tuples?
In Python, list and tuple are a class of data structures that can store one or more objects or values. A list is used to store multiple items in one variable and can be created using square brackets. Similarly, tuples also can store multiple items in a single variable and can be declared using parentheses.
What is list and example?
What is a List? A list is an ordered data structure with elements separated by a comma and enclosed within square brackets. For example, list1 and list2 shown below contains a single type of data. Here, list1 has integers while list2 has strings. Lists can also store mixed data types as shown in the list3 here.
What is list and its types?
The three list types. There are three list types in HTML: unordered list — used to group a set of related items in no particular order. ordered list — used to group a set of related items in a specific order. description list — used to display name/value pairs such as terms and definitions.
What are the types of the lists?
An example of the three list types, which are unordered list, ordered list, and definition list.
What is an example of syntax in computer?
In other words, it means using character structures that a computer can interpret. For example, if a user tries to execute a command without proper syntax, the compiler finds this error and generates a syntax error, usually causing the program to fail.
What is the syntax of a Python class?
A class in Python can be defined using the class keyword. As per the syntax above, a class is defined using the class keyword followed by the class name and : operator after the class name, which allows you to continue in the next indented line to define class members.
What is class with syntax and example?
In object-oriented programming, a class is an extensible program-code-template for creating objects, providing initial values for state (member variables) and implementations of behavior (member functions or methods).
What Is syntax with example?
Syntax in English sets forth a specific order for grammatical elements like subjects, verbs, direct and indirect objects, etc. For example, if a sentence has a verb, direct object, and subject, the proper order is subject → verb → direct object.
What Is syntax format?
Syntax Formatting uses rich text formatting based on program information. Source Insight uses information gathered from its parsers to format source code. Identifiers can be displayed in different fonts or font sizes, along with a variety of effects such as bold and italics.
Why is syntax important?
“Syntax skills help us understand how sentences work—the meanings behind word order, structure, and punctuation. By providing support for developing syntax skills, we can help readers understand increasingly complex texts” (Learner Variability Project).
What Is syntax elements?
Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics).